Logistics managers relying on legacy WMS or ERP systems that don’t connect with modern tools struggle to adjust inventory levels and respond quickly to order changes or shipment delays. Disconnected warehouse, transport, and sales systems further lead to missed delivery windows, higher labor costs, and inventory inaccuracies.
AI addresses these challenges by automating repetitive tasks like picking, packing, while providing real-time visibility into inventory and workflows. In fact, 55% of supply chain leaders are increasing their technology investments, with 88% planning to spend over $1 million.
How can your warehouse put AI to work to increase profitability?
In this guide, we’ll go through all that you need to know about AI in warehouse management, its use cases, real-life case studies, and how to integrate it into your warehouse operations.
What Is AI in Warehouse Management?
AI in warehouse management utilizes machine learning, robotics, and computer vision to automate processes, optimize operations, and deliver real-time insights.
For example, a logistics manager may struggle with inventory inaccuracies that lead to stockouts or overstocking. With AI, machine learning models can forecast demand and automatically adjust stock levels, and reduce the risk of stockouts or minimize excess inventory.
It ensures smoother operations, reduces costs, and improves fulfillment accuracy, which helps meet customer delivery expectations more efficiently.
Traditional Automation vs. Manual Processes
To better understand the value AI provides, let’s compare how AI-powered warehouse management differs from traditional methods:
| Aspect | Manual Processes | Traditional Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Speed and efficiency | Slower, dependent on human effort | Faster, consistent task execution |
| Accuracy | Higher risk of human errors | Reduced errors in repetitive tasks |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale without adding labor | Easier to scale with minimal added effort |
| Labor dependency | High reliance on workforce availability | Lower dependency; automates repetitive work |
| Cost over time | Lower upfront cost, higher long-term labor costs | Higher upfront cost, lower long-term operational costs |
| Flexibility | Easily adaptable to changes | Limited; changes require system adjustments |
| Data and insights | Limited or no real-time tracking | Provides structured data for analysis |
| Training needs | Requires training for new employees | Requires initial training for system use |
Core Technologies Powering Warehouse AI
Warehouse AI relies on key technologies such as machine learning, robotics, and computer vision, which work together to automate tasks, optimize inventory management, and improve order fulfillment accuracy.
Machine Learning And Predictive Analytics
Inaccurate demand forecasting can lead to costly overstocking, frequent stockouts, and poor customer experience, which directly impact revenue and efficiency. Machine learning models forecast demand and optimize inventory. Analyzing historical data and market trends, warehouses can predict future demand so that stock levels are appropriate without overstocking or running out of key items.
For example, Walmart uses machine learning for demand forecasting, which has led to an increase in stock accuracy and reduced out-of-stock situations by 10%.
Suggested read: 7 Ways Demand Forecasting With AI is Boosting Business Success
Computer Vision
In large warehouses, it’s difficult to manually count inventory or spot damaged items. So, computer vision automates visual inspection and inventory tracking. AI-powered cameras scan barcodes, detect product anomalies, and track inventory in real-time.
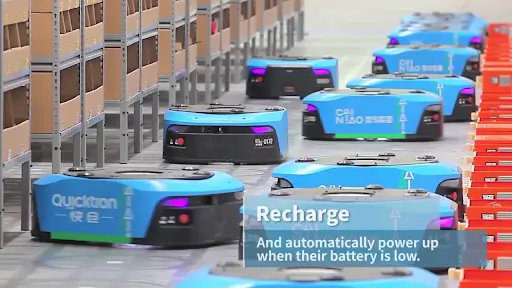
Robotics And Automation
AI robots can now handle repetitive tasks like picking, sorting, and packing, which reduces manual labor costs and improves operational speed. These robots can adapt to the warehouse layout and changes in order demand, enhancing efficiency with minimal human oversight.
Large Language Models (LLMs) help warehouse employees access critical information quickly. AI chatbots and natural language processing (NLP) systems let workers query databases and SOPs, and speed up restocking, order fulfillment, and troubleshooting.
How is AI Changing Warehouse Operations
AI in warehouse management addresses some of the biggest fulfillment pain points, from slow picking and inefficient layouts to high error rates and overworked staff. Plus, it makes your existing operations more efficient.
Key Business Drivers For AI Adoption In Warehouses
The push toward AI in warehouse management helps managers survive in an industry where speed, efficiency, and resilience directly impact revenue.
Rising customer expectations
E-commerce has redefined “fast.” Recent data from ShipStation shows that 55% of shoppers are willing to pay extra for same‑day or next‑day delivery.
When those expectations are not met, the fallout is immediate.
In practice, this means a warehouse that cannot keep up with fulfillment speed risks not only losing customers but also tarnishing its brand reputation. AI helps prevent this by analyzing order patterns, predicting fulfillment bottlenecks, and dynamically optimizing picking routes and schedules, so warehouses can meet rising service expectations without overburdening their teams.
Supply chain disruptions
Global supply chain disruptions make it far more difficult for warehouses to manage inventory and meet fluctuating demand. When shipments are delayed or suppliers cannot deliver on time, warehouses face cascading problems, from stockouts that lead to lost sales and unhappy customers to overstocking that ties up capital and storage space.
AI fills this gap. Predictive maintenance and demand forecasting help warehouses mitigate risks associated with stockouts, overstocking, and sudden demand spikes.
Labor shortages and cost pressures
McKinsey report estimates that disruptions lasting a month or more now occur every 3.7 years on average, costing companies 6–10% of annual revenue.
AI-driven labor optimization tools help warehouses reduce their reliance on manual labor by automating repetitive tasks. For instance, AI scheduling systems can predict peak periods and allocate resources efficiently, which results in reduced labor costs.
Benefits of Using AI in Warehouse Management
Running a warehouse without AI often means relying on manual processes, reactive decision-making, and stretched resources, all of which slow down operations and increase costs. Here’s how AI changes that.
Improved Inventory Accuracy
Without AI, inventory tracking is prone to human error, delayed updates, and blind spots that lead to stockouts or overstocking. With AI, inventory is tracked in real time using automated systems that provide accurate, up-to-date visibility across all storage locations, ensuring the right products are available when needed.
Faster Decision-Making
Traditional decision-making often depends on manual reporting and gut instincts, which delay responses to demand changes or disruptions. AI-driven analytics change this by delivering real-time insights that help managers adjust inventory, labor, and workflows on the fly.
Optimized Workforce Management
Manual scheduling often results in overstaffing during quiet periods and staff shortages during peak times, driving up costs and hurting productivity. AI tools use demand forecasts and performance data to create optimized shift schedules so that the right number of workers are deployed at the right times.
Reduced Operational Costs
In a traditional setup, repetitive manual tasks like picking, sorting, and replenishment consume significant time and labor costs. AI-powered automation takes over these repetitive tasks, freeing up employees for higher-value work, reducing operational expenses, and boosting overall throughput.
Optimize Last-Mile Delivery
By 2024, last-mile delivery was expected to account for 53% of overall shipping costs, stressing the need for optimization. AI can optimize last-mile delivery routes based on real-time data, improving delivery speed and reducing costs.
AI Use Cases in Warehouse Management
AI is changing warehouse operations with applications across inventory management, order fulfillment, workforce optimization, and more. Here’s how:
Inventory Optimization And Forecasting
AI models predict demand based on historical sales data, seasonality, and external factors. This means warehouse managers can maintain accurate stock levels, reducing both stockouts and overstocking.
Amazon’s AI-driven warehouse optimization
For example, Amazon’s AI-powered warehouse service helps sellers optimize inventory distribution, reducing transportation costs and improving delivery times by 20%.
Intelligent Order Picking And Routing
AI-powered robots and systems optimize picking routes within warehouses, reducing travel time for workers. By automating these processes, AI increases order fulfillment speed and accuracy.
Alibaba’s AGVs enhance warehouse efficiency
Alibaba’s Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have reduced order picking times by 25% and boosted its capacity to handle larger volumes during peak demand.
Workforce Scheduling And Labor Planning
AI analyzes data on warehouse activity and demand patterns to schedule labor so that the right number of workers are on shift during peak times.
AI improves labor efficiency in logistics
For example, Kuehne + Nagel, a global logistics provider, uses AI-based workforce management systems to cut overtime costs, ensure optimal labor utilization, and reduce burnout.
Real-Time Supply Chain Visibility
AI-powered analytics can provide real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies for proactive management. It changes supply chains by improving demand sensing, inventory optimization, procurement, and risk management while enabling sustainability, transparency, and automation.
DHL uses AI for real-time operational visibility
For example, DHL employs AI-based dashboards for real-time visibility into operations, which let managers address issues immediately and optimize workflow, reducing delays.
Suggested read: Revolutionalizing Supply Chains: AI Consulting Unveiled
Automated Quality Checks And Defect Detection
Using computer vision, AI systems inspect products during packing and sorting. These systems can detect defects, packaging errors, or misidentified items, automatically flagging issues for review.
Zebra Technologies enhances stock tracking with AI
For instance, Zebra Technologies uses AI-based computer vision systems to streamline product scanning, which improves stock tracking accuracy and decreases human error.
Autonomous Systems And Robotics Collaboration
Automation in logistics is not limited to picking, packing, or mitigating supply chain disruptions. It also optimizes back-office operations, invoice processing, payment tracking, and cash flow management, with greater speed and accuracy than manual methods.
Gallium Technologies streamlining receivables with AI
For example, Gallium Technologies implemented RTS Labs’s AI-driven solution for accounts receivable management as they struggled with slow payments and inefficient cash flow.

RTS Labs developed a scalable, data-powered solution for them with:
- Industry benchmarking for credit collections
- Automated accounts receivable management
- Early payment issue detection to improve cash flow
Here’s the full case study.
Challenges to Adopting AI in Warehouse Environments
Adopting AI in warehouse management comes with its own set of challenges, which warehouse managers must address for successful implementation.
Data Quality And Infrastructure Limitations
AI relies on high-quality data to make accurate predictions. Poor data quality can result in incorrect forecasts and inefficient processes. Ensuring data consistency and integrity across the warehouse’s systems is essential for AI to function effectively.
Integration With Legacy Wms And Erp Systems
Many warehouses still rely on outdated warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms. Integrating AI into these legacy systems can be costly and time-consuming. Overcoming this challenge requires careful planning and often requires custom-built solutions.
Change Management And Workforce Adoption
Introducing AI into warehouse operations means adjusting workflows and retraining employees. Ensuring that workers are comfortable with new technologies is crucial. Providing adequate training and clear communication about AI’s role in improving efficiency can help reduce resistance.
Concerns Around Cost, Roi, And Implementation Time
The initial investment in AI technology can be significant. Warehouse managers must ensure they have a clear ROI strategy before proceeding. Many organizations are hesitant due to the perceived high costs and long implementation timelines.
A report from the logistics and supply chain association MHI highlights that only 16% of organizations say they’re unlikely to adopt AI technologies within the next five years, reflecting the growing recognition of AI’s role in overcoming warehouse challenges. However, despite this enthusiasm, adoption rates remain slow due to the complexity and cost of implementation.
How to Get Started With AI in Your Warehouse
Follow this step-by-step approach to overcome the challenges of AI adoption and maximize the benefits of automation and optimization.
1. Secure Executive Buy-In And Define Objectives
Before adopting AI, it’s important to gain buy-in from key decision-makers as they ensure necessary resources are allocated and the project aligns with business goals.
For this, define clear objectives for AI implementation, such as reducing operational costs, improving inventory accuracy, or increasing order fulfillment speed. By setting specific, measurable goals, the AI implementation process becomes more focused and aligned with the organization’s strategic vision.
2. Assess Current Processes And Identify Use Cases
Review your workflows, from inventory management to order fulfillment, and evaluate where inefficiencies or challenges arise. Identify specific use cases for AI, such as predictive inventory management, robotic automation, or workforce optimization, that align with your operational goals.
Maximize ROI with tailored AI consulting
We work with you to assess current processes and pinpoint the most promising use cases for AI in your warehouse. Our AI Consulting services help you prioritize areas that will yield the highest ROI and operational efficiency.
3. Data Collection And Integration
AI relies heavily on data to deliver insights and make informed decisions. Collecting accurate, consistent, and comprehensive data from various sources within your warehouse (inventory records, order history, worker performance, etc.) is crucial for AI success. Integration of data from existing warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems is necessary to ensure that AI has access to the right data at the right time.
Streamline AI integration with clean, structured data
We support data collection and integration by helping you structure and organize your data. Our team works with you to ensure data quality and integrate AI solutions with your existing systems for smooth operations.
4. Select AI Technologies and Partners
Choosing the right AI consulting firm depends on your use cases and technologies like machine learning, robotics, computer vision, or natural language processing (NLP). Work with AI partners who have a proven track record in warehouse management systems and AI-driven solutions.
5. Pilot and Scale
Run a pilot project to test the AI systems and validate their effectiveness. A small-scale pilot allows you to identify any potential challenges or shortcomings before fully rolling out the system across your entire operation.
From pilot to full-scale AI implementation
We guide you through the pilot phase, helping you set clear metrics for success and troubleshooting any issues that arise. Once the pilot is complete, we help scale the AI solution across your warehouse operations, ensuring a seamless transition and quick adoption.
6. Workforce Training and Change Management
AI adoption often involves significant changes to daily workflows, which can lead to resistance from employees. Provide training and clear communication to help employees understand how AI will complement their work rather than replace it.
Empowering teams with AI readiness training
We work with your team to build AI literacy with change management policies and training so employees know how to work alongside AI systems.
7. Monitor, Optimize, and Expand
After implementation, continuous monitoring is important to ensure the AI system is working as intended. Regularly assess performance against your defined objectives, optimize processes where needed, and scale the solution to other areas or locations.
Continuous support for long-term AI success
Our process involves providing ongoing support to monitor AI system performance and help you refine AI models, update systems, and expand AI solutions as your business grows.
Implement AI in Warehouse Management with RTS Labs
At RTS Labs, we partner with logistics organizations to implement AI solutions that address critical operational challenges. Our expertise spans improving real-time visibility, inventory accuracy, and streamlining workforce planning, all tailored to the unique requirements of your warehouse operations.
Interested in understanding how AI can deliver measurable efficiency gains for your facilities?
Schedule a demo with RTS Labs today to explore solutions designed for your operational priorities.
FAQs
1. What are the most common AI tools used in warehouse management?
Common tools include machine learning for demand forecasting, computer vision for quality control, and robotics for automation in picking/packing.
2. Can small warehouses adopt AI, or is it just for enterprises?
Small warehouses can benefit from AI-driven tools like predictive inventory management and automation systems, which help reduce manual labor and improve efficiency.
3. How long does it take to implement an AI solution in warehouse operations?
Implementation time varies but typically takes a few months for small-scale solutions. Full-scale AI integration may take longer, especially when integrating with legacy systems.