Last-mile delivery has quietly become the most expensive and least controllable part of modern logistics, representing up to half of total delivery costs.
Traditional last-mile delivery systems were never designed for today’s operating reality. Static route planning, rule-based dispatching, and manual coordination break down under demand volatility, urban congestion, labor shortages, and rising service expectations. As volumes scale, even small inefficiencies compound, turning the last mile into the single biggest drag on logistics performance and profitability.
AI changes last-mile delivery from a reactive operation into a predictive, adaptive system. Instead of planning routes once a day and reacting to disruptions after they happen, AI continuously optimizes routing, dispatch, ETAs, and customer communication in real time.
This article breaks down what AI-powered last-mile delivery actually looks like in practice, where it delivers measurable ROI, and how organizations can implement it successfully, without getting stuck in pilots or fragmented tools.
What Is AI-Powered Last-Mile Delivery?
AI-powered last-mile delivery is the use of machine learning, optimization algorithms, real-time data, and intelligent automation to continuously manage how orders are routed, dispatched, delivered, and communicated to customers.
Traditional last-mile systems rely on static rules and fixed routes. But AI-driven delivery systems learn from live conditions, such as traffic congestion, driver availability, order density, weather, customer behavior, and historical delivery outcomes. Decisions are recalculated dynamically, allowing operations teams to intervene before delays, missed deliveries, or cost overruns occur.
In practice, this means last-mile delivery shifts from reactive firefighting to predictive control.
- Routes adjust in real time,
- ETAs become probabilistic,
- Exceptions are flagged early, and
- Customer communication is automated based on actual delivery risk.
This distinction is critical. Many organizations invest in routing tools or analytics dashboards, but fail to integrate AI deeply into operational workflows. AI delivers value only when it is embedded directly into dispatch, routing, warehouse coordination, and customer systems, rather than being layered on top as a reporting add-on.
AI-powered last-mile delivery is therefore less about individual models and more about decision systems. These systems connect data pipelines, optimization engines, and operational tools, so that every delivery decision improves margin, reliability, and customer experience over time.
Why Last-Mile Delivery Is the Biggest Bottleneck in Logistics
For most logistics and retail leaders, last-mile delivery isn’t a downstream execution problem. It is the primary constraint on margin, scale, and customer experience. Last-mile delivery fails because its systems are not designed to sense, decide, and act dynamically.
No Linear Economies of Scale
The challenge starts with economics. As delivery volumes increase, last-mile costs do not scale linearly. Urban congestion, fragmented drop density, labor shortages, and narrow delivery windows compound complexity, pushing cost per delivery upward even as customers expect faster, cheaper service. Traditional route-planning systems, built for static conditions, simply cannot adapt to this volatility in real time.
Operational Uncertainty
Operationally, the last mile is where uncertainty concentrates. Traffic conditions change by the minute. Customer availability is unpredictable. Driver schedules shift. Weather disruptions cascade across routes.
When dispatch decisions are locked in hours earlier, even small disruptions propagate downstream, resulting in missed SLAs, reattempts, overtime labor, and customer dissatisfaction.
Lack of Visibility
Visibility is another structural weakness. Many enterprises still operate with delayed or partial insight into what is happening on the road. By the time exceptions surface in dashboards, the opportunity to intervene has already passed. This lack of real-time awareness forces teams into reactive firefighting rather than proactive optimization.
ESG Concerns
Sustainability pressures further intensify the bottleneck. Fuel inefficiency, unnecessary mileage, and failed deliveries directly increase emissions, making last-mile performance a board-level concern tied to ESG commitments, not just logistics KPIs.
Factors Driving the Rising Cost of Last-Mile Delivery
Last-mile delivery costs don’t rise because of a single failure point. They increase because multiple pressure layers, such as customer expectations, on-ground execution realities, and technical constraints, compound and reinforce each other and erode efficiency at scale.
Shifting Customer Expectations
From the customer side, delivery expectations have shifted faster than operational models can adapt. Same-day and next-day delivery windows, time-slot precision, and real-time status updates are baseline expectations.
Every failed delivery attempt due to customer unavailability triggers reattempts, reverse logistics, and support overhead, inflating cost per order while degrading customer trust. Flexible return policies further amplify this effect, turning last-mile networks into two-way systems without corresponding intelligence to manage the complexity.
Operational volatility
On the field operations side, cost pressure intensifies through low drop density, labor volatility, and urban constraints. Delivery routes are increasingly fragmented, especially in dense metros where parking restrictions, traffic congestion, and access limitations reduce driver productivity.
At the same time, labor shortages and rising wages force operators to stretch limited capacity across growing delivery volumes. Static dispatch plans quickly become obsolete once real-world conditions intervene, leading to overtime, missed SLAs, and inefficient asset utilization.
Technical Obsoleteness
Many enterprises still rely on disconnected ERP, TMS, WMS, and CRM systems that provide delayed or incomplete visibility into delivery operations. Route plans are generated using static rules and historical averages, unable to adjust to live disruptions. Exception handling remains manual, requiring human intervention after problems have already occurred.
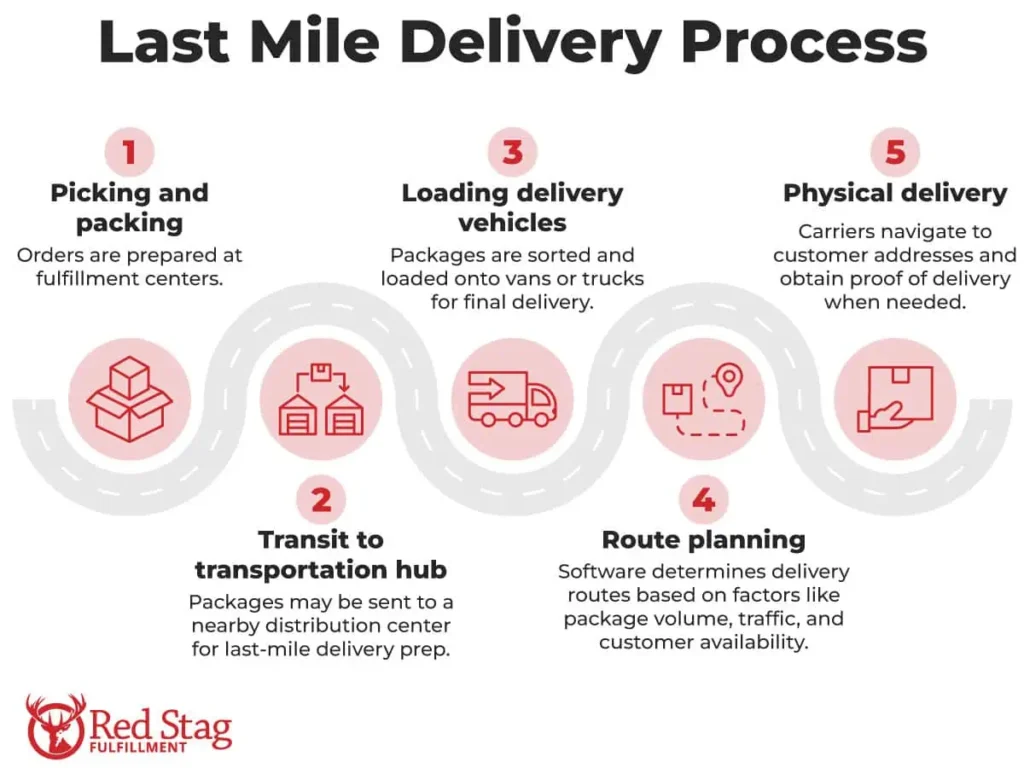
How AI Transforms Last-Mile Delivery Operations
AI fundamentally changes last-mile delivery by shifting operations from reactive execution to predictive, continuously optimized decision-making. Instead of relying on static route plans and manual interventions after delays occur, AI-enabled systems sense disruptions in real time, recalculate optimal actions, and keep deliveries moving with minimal friction.
Dynamic Route Optimization
AI models continuously adjust routes based on live traffic, weather, delivery density, driver availability, and customer constraints to reduce idle time, cut fuel consumption, and improve drop density, often without adding fleet capacity. Enterprises working with us typically see that even small routing improvements compound quickly at scale, translating into meaningful cost savings across thousands of daily deliveries.
For instance, we helped a sports equipment manufacturer scale by removing the infrastructure burden and automating processes to reduce costs by 25%.
Predictive ETAs and Intelligent Dispatching
AI systems generate more accurate delivery windows and proactively rebalance loads when delays are likely, by learning from historical delivery patterns and real-time signals. This prevents cascading failures, like missed slots, reattempts, and customer escalations, before they occur. Dispatch teams move from firefighting to exception oversight, focusing only on high-impact anomalies.
Automated Exception Handling
Missed deliveries, address issues, or vehicle breakdowns no longer require manual triage. AI models detect anomalies as they emerge, trigger rerouting or reassignment, and notify customers automatically. We integrate these capabilities directly into existing TMS and customer communication workflows to make sure AI decisions are actionable and not just analytical.
Warehouse-to-door Coordination
Inventory availability, pick-pack timing, and outbound dispatch are synchronized with last-mile capacity, reducing dwell time and failed handoffs. Real-time customer communication powered by predictive insights keeps recipients informed and available, further reducing reattempt rates.
AI turns last-mile delivery into a system that learns and improves continuously. RTS Labs’ role is to ensure this intelligence is embedded end-to-end across data pipelines, optimization models, and production systems, so transformation delivers sustained impact, not short-lived pilot gains.
Core Technologies Powering AI Last-Mile Delivery
AI-driven last-mile delivery is not a single model or tool, but a stack of tightly integrated technologies working together to sense conditions, make decisions, and execute actions in real time. What differentiates high-performing enterprises from stalled pilots is how well these technologies are orchestrated inside live operations.
Machine Learning for Demand and Delivery Prediction
These models forecast order volumes, delivery density, service-time variability, and failure probability at a hyper-local level. Instead of planning routes based on averages, enterprises plan based on probability distributions, which dramatically improves ETA accuracy and capacity planning. We typically embed these models directly into planning workflows so predictions immediately influence dispatch and load decisions.
Optimization Algorithms for Routing And Scheduling
AI-driven optimizers don’t work like basic rule-based planners. These tools evaluate millions of route permutations under real-world constraints, such as traffic, time windows, vehicle capacity, driver hours, and cost trade-offs. When disruptions occur, the optimizer recalculates in seconds, enabling continuous re-optimization rather than end-of-day corrections.
IoT and Telematics for Real-time Visibility
IoT and telematics provide real-time visibility into fleet location, vehicle health, and driver behavior. These signals feed AI systems with live context, allowing models to adapt instantly. We integrate telematics data into unified pipelines so routing, ETAs, and customer updates are always based on current conditions.
Computer Vision for Intelligence
Computer vision adds intelligence at the edge, supporting address verification, proof of delivery, damage detection, and compliance checks. This reduces disputes, speeds reconciliation, and lowers operational leakage in high-volume delivery environments.
Gen AI and Decision Copilots
Generative AI and decision copilots are increasingly being layered on top of these systems. Dispatchers and operations managers interact with AI through natural language, asking why routes changed, what risks are emerging, or how to rebalance capacity. We design these copilots to augment human judgment, trust.
Individually, these technologies create incremental gains. Integrated correctly, they form a self-optimizing last-mile system, one that learns, adapts, and improves with every delivery. Our value lies here, in engineering this integration end-to-end, ensuring each technology reinforces the others inside production workflows.
| Rising Cost Driver |
Why It Increases Last-Mile Costs |
How AI Transforms and Reduces Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Shifting Customer Expectations | Same-day and next-day delivery expectations compress planning windows.
Failed delivery attempts trigger reattempts, reverse logistics, and support costs. Flexible return policies increase two-way traffic. |
Predictive ETAs and Customer Intelligence
AI predicts customer availability to prevent failed deliveries. Generates accurate time windows using real-time and historical data. Automates customer updates to reduce reattempts and support tickets. |
| Operational Volatility (Field and Driver Constraints) | Low drop density and fragmented routes reduce driver productivity.
Urban access limitations such as parking and congestion inflate fuel and labor hours. Rising wages and labor shortages stretch operational capacity. |
Dynamic Route Optimization
Optimizes routes using weather, traffic, access rules, fleet mix, and delivery density. Cuts idle time and fuel usage while increasing drops per hour. Balances workloads with intelligent dispatching. |
| Technical Obsoleteness (Disconnected Systems) | ERP, WMS, TMS, and CRM operate in silos, creating poor visibility.
Static routing models cannot adapt to live events. Exception handling remains manual and reactive. |
AI-Driven Operations and Automated Exception Handling
Real-time anomaly detection triggers automatic rerouting or reassignment. AI copilots support dispatchers with predictive decision prompts. Computer vision and IoT improve address accuracy, proof-of-delivery validation, and in-route visibility. |
| Two-Way Delivery Complexity (Returns and Exchanges) | Reverse logistics lack optimization intelligence.
Returned items force additional trips and capacity reallocation. |
Reverse Logistics Optimization
AI clusters return pickups with forward delivery routes. Predicts return volumes to plan capacity days ahead. |
| Warehouse-to-Door Disconnect | Poor synchronization between pick-pack cycles, dispatch times, and route constraints.
Inventory mismatches cause delays or failed handoffs. |
Warehouse and Last-Mile Coordination
AI aligns warehouse readiness with last-mile delivery capacity. Predictive insights reduce dwell time and improve handoffs. |
| Scaling Inefficiency (Static Processes) | Small disruptions cascade across thousands of delivery stops.
Human-only dispatching cannot operate effectively at delivery scale. |
Self-Optimizing Delivery Network
AI learns from every delivery to improve continuously. Shifts teams from crisis management to proactive exception management. |
6 High-Impact Use Cases of AI in Last-Mile Delivery
AI delivers real value in last-mile delivery when it is applied to specific, high-friction operational decisions. The most successful enterprises focus on a small number of use cases that directly reduce cost, improve delivery reliability, and protect customer experience.
Below are the use cases where AI consistently produces measurable ROI and helps enterprises move from pilots to production.
#1 Real-time Route Optimization
Instead of locking routes hours in advance, AI continuously re-optimizes based on traffic, weather, delivery progress, and new orders to reduce fuel spend, cut overtime, and improve on-time delivery, especially in dense urban routes. We typically embed these optimizers directly into existing TMS platforms so route changes flow seamlessly to drivers without operational disruption.
Related Read: AI Route Optimization
#2 Predictive Delivery Windows and ETAs
Predictive delivery windows and ETAs address one of the most expensive last-mile failures, i.e., missed deliveries. By modeling stop-level service time, customer availability, and historical delay patterns, AI narrows delivery windows and proactively adjusts schedules, reducing reattempts and increasing first-attempt delivery success. These parameters are critical for e-commerce and B2C logistics.
#3 Smart Driver Allocation and Load Balancing
Smart driver allocation and load balancing help enterprises operate with tighter margins despite labor shortages. AI models match drivers to routes based on skill, familiarity, historical performance, and fatigue risk. We combine this with workforce analytics so planners can rebalance capacity dynamically rather than reacting after service failures occur.
#4 Failed Delivery Prediction and Prevention
AI flags deliveries at risk of failure due to address issues, customer behavior, or route congestion before trucks leave the depot. Operations teams can intervene early by rescheduling, rerouting, or prompting customer confirmation, significantly reducing downstream cost.
#5 Returns and Reverse Logistics Optimization
Returns and reverse logistics optimization have become increasingly important as return rates rise. AI clusters pickups, predicts return volume, and integrates reverse flows into forward routes to lower cost per return and improve asset utilization without adding fleet capacity.
#6 Automated Customer Communication
AI-driven messaging updates customers in real time, manages delivery preferences, and reduces inbound support volume. RTS Labs integrates these workflows with CRM systems so customer experience improves without adding operational overhead.
Challenges in Implementing AI for Last-Mile Delivery
While AI has clear potential to reduce last-mile costs and improve delivery performance, implementation is where most initiatives stall. The challenge is rarely the algorithm itself. It’s the operational, data, and organizational realities of last-mile delivery that make execution difficult.
- Poor Data Quality and Siloed Systems: Last-mile operations depend on inputs from multiple sources, including order management, TMS, WMS, fleet telematics, driver apps, and customer data. When this data is incomplete, delayed, or inconsistent, AI models cannot generate reliable routing decisions or ETAs. In practice, this leads to intelligent systems that still require heavy manual intervention.
- Integration With Existing Logistics Platform: AI must operate inside real workflows, dispatching tools, route planners, driver interfaces, and customer communication systems. Without tight integration, insights remain disconnected from execution, limiting ROI and slowing adoption.
- Scaling from Pilot to Production: Many organizations validate AI models on small datasets or limited geographies but struggle when volumes increase, conditions change, or real-world exceptions occur. Without MLOps, monitoring, and retraining pipelines, model performance degrades quickly in live delivery environments.
- Human Adoption Challenge: Dispatchers, drivers, and operations managers may distrust automated recommendations if systems feel opaque or disruptive. When change management is overlooked, AI insights are ignored even if they are accurate.
- Maintaining Model Accuracy: Finally, maintaining model accuracy in dynamic conditions, such as traffic, weather, labor availability, and demand volatility, requires continuous feedback loops. Static models fail in last-mile delivery, where conditions change hourly, not quarterly.
How to Implement AI-Driven Last-Mile Delivery Successfully
Successful AI adoption in last-mile delivery follows a disciplined execution path. Organizations that see measurable ROI start with operational clarity, data readiness, and a realistic deployment plan.
Step 1: Assessing Operational Maturity and Data Readiness
Leaders need a clear view of where delivery data lives, how reliable it is, and which systems must be connected. Without this foundation, AI models inherit the same blind spots as manual planning.
Step 2: Identifying High-Impact Automation Opportunities
Rather than attempting to ‘AI-enable everything,’ effective teams prioritize use cases tied to cost and service KPIs like route optimization, ETA prediction, or failed-delivery prevention for early wins that build internal confidence and executive buy-in.
Step 3: Building Unified Data Pipelines
With priorities set, organizations must build unified data pipelines that stream real-time signals into AI models. This is the inflection point where last-mile operations shift from static planning to adaptive decision-making.
Step 4: Deploying AI models
Deploying AI models and optimization engines directly into workflows is the next step. Routing intelligence must feed dispatch systems, driver apps must receive dynamic updates, and customer notifications must reflect real-time conditions. AI only delivers value when it acts, not when it sits in dashboards.
Step 5: Pilot, Measure ROI, And Scale
From there, teams should pilot, measure ROI, and scale deliberately. Controlled rollouts across regions or delivery types allow organizations to validate cost savings, on-time performance, and customer satisfaction before expanding.
Step 6: Continuous Optimization
Finally, success depends on continuous optimization. Last-mile AI requires ongoing monitoring, retraining, and feedback loops to stay accurate as demand patterns, traffic conditions, and labor availability change.
RTS Labs supports this entire journey, helping enterprises move beyond pilots and build AI-driven last-mile systems that perform reliably at scale.
Future Trends in AI Last-Mile Delivery
The next phase of last-mile delivery will be about autonomous, decision-driven logistics systems that continuously adapt without manual intervention. A few notable trends in AI last-mile delivery include:
- Rise of AI decision agents that can rebalance routes, reassign drivers, and resolve delivery exceptions automatically as conditions change. Instead of dispatch teams reacting to disruptions, these systems anticipate issues and act in real time.
- Carbon-aware routing AI optimizes deliveries not only for time and cost but also for emissions. As sustainability reporting becomes mandatory across regions, logistics leaders are using AI to balance service-level commitments with fuel usage and environmental impact.
- Momentum around AI-powered micro-fulfillment orchestration is where last-mile decisions are tightly coupled with warehouse location, inventory placement, and order batching. This creates a closed loop between fulfillment and delivery, reducing travel distance, improving drop density, and lowering per-order costs.
- Generative AI copilots for dispatch and operations leaders are moving from experimentation into production. These copilots surface insights, recommend actions, and explain trade-offs in plain language, helping human operators supervise complex delivery networks without slowing decisions.
Enterprises that treat these trends as a long-term strategy are the ones building defensible last-mile advantages.
How RTS Labs Helps Build AI-Driven Last-Mile Delivery Systems
Successful AI last-mile delivery comes from engineering AI into the operational core of logistics systems. This is where many initiatives fail, and where RTS Labs differentiates.
RTS Labs works with logistics, retail, and supply chain leaders to unify fragmented delivery data across TMS, WMS, ERPs, telematics platforms, and customer systems. This data foundation enables real-time decision-making, without which AI models cannot operate reliably in the field.
From there, RTS Labs designs and deploys custom optimization and predictive models tailored to real-world delivery constraints: traffic volatility, driver availability, service-level agreements, urban access rules, and customer behavior. These models are not static. They are continuously monitored, retrained, and governed using production-grade MLOps pipelines.
For organizations exploring AI-driven dispatching and exception management, RTS Labs builds LLM-powered copilots and decision agents that integrate directly into existing workflows, rather than forcing teams to adopt new tools. This dramatically accelerates adoption while maintaining control, auditability, and explainability.
Critically, RTS Labs supports the full lifecycle from strategy and feasibility assessment to deployment, monitoring, and optimization for AI systems to remain accurate, cost-efficient, and trusted as delivery networks evolve.
Turning Last-Mile Complexity Into a Competitive Advantage
Last-mile delivery is no longer just a logistics challenge. It is a profitability, customer experience, and resilience challenge. As costs rise and delivery expectations tighten, manual planning and static systems are no longer viable at scale.
AI-powered last-mile delivery enables enterprises to shift from reactive execution to predictive, adaptive operations, reducing failed deliveries, improving asset utilization, and restoring margin control. But realizing this value requires more than algorithms. It requires strong data foundations, deep systems integration, production-grade AI engineering, and disciplined execution.
RTS Labs helps organizations make this shift, turning last-mile delivery from a cost center into a strategic advantage through AI systems that actually work in production. If your organization is exploring AI-driven last-mile optimization, the next step isn’t another pilot, but a clear execution roadmap.
RTS Labs partners with leaders to design, build, and scale AI delivery systems that deliver measurable ROI in the real world.
FAQs
1. How does AI actually reduce last-mile delivery costs?
AI reduces last-mile costs by dynamically optimizing routes, improving drop density, predicting failed deliveries before they occur, and automating dispatch decisions, lowering fuel spend, labor inefficiencies, and reattempt rates simultaneously.
2. What data is required to implement AI in last-mile delivery?
Effective AI last-mile systems require unified data from TMS, WMS, ERP, fleet telematics, order management, traffic, weather, and customer interaction systems. Without this integration, AI models cannot operate reliably in production.
3. Can AI last-mile delivery systems work with legacy logistics platforms?
Yes, but only when designed correctly. Enterprise AI must be integrated via APIs and data pipelines into existing TMS, WMS, and ERP systems. This integration challenge is often harder than model development itself.
4. How long does it take to see ROI from AI last-mile delivery?
Most organizations see measurable ROI within 3–6 months when AI is deployed against high-impact use cases like route optimization, ETA prediction, and exception handling, provided the data foundation is in place.
5. Why do many AI last-mile delivery pilots fail to scale?
They fail due to poor data readiness, lack of MLOps, weak system integration, and resistance from dispatch and operations teams. AI succeeds only when embedded into real workflows, not run as a parallel experiment.






