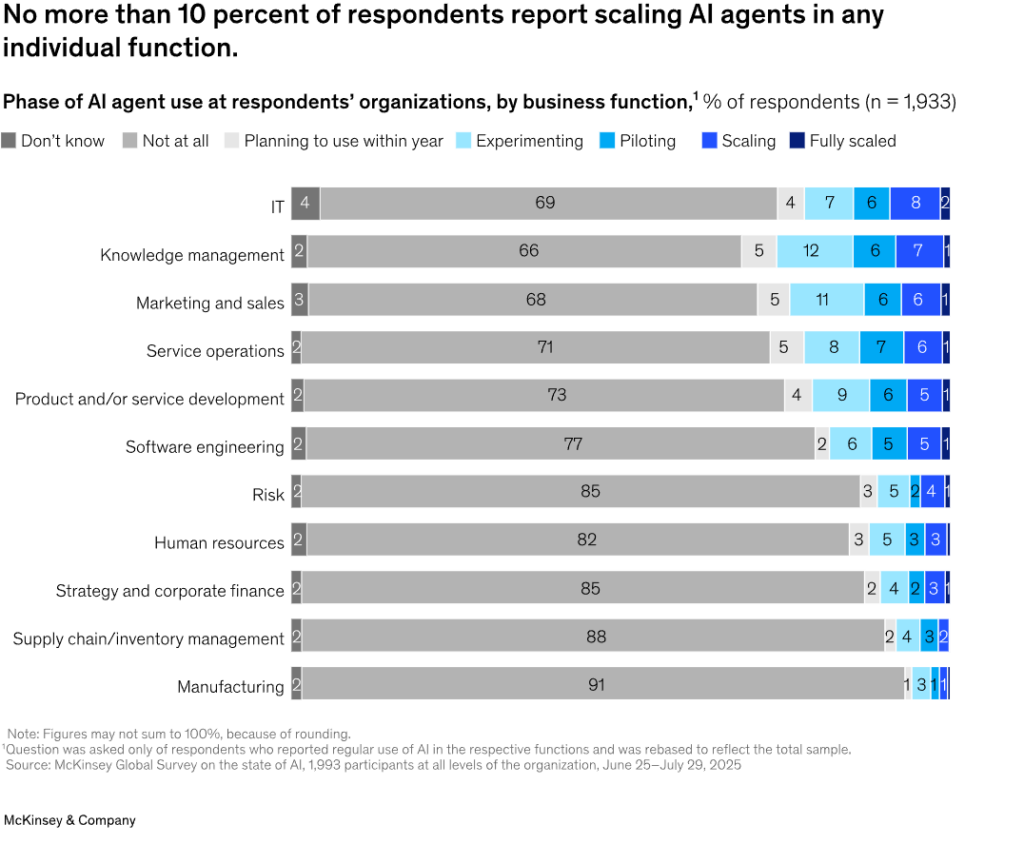
88% of enterprises reported using AI in at least one business function, but no more than 10% report scaling it, finds McKinsey’s The State of AI in 2025: Agents, Innovation, and Transformation report. Enterprises aren’t able to scale or succeed at AI because they automate assumptions instead of reality.
Across large organizations, work rarely follows the clean paths shown in documentation. As organizations scale across systems, teams, and geographies, processes evolve informally. Exceptions become the norm, manual interventions proliferate, and regional variations quietly reshape execution.
Processes sprawl across ERPs, collaboration tools, approval chains, and regional workarounds. Over time, what should happen diverges sharply from what actually happens. When AI or automation is layered on top of this misalignment, the result is stalled initiatives, brittle workflows, and disappointing ROI.
AI process mapping has emerged as a corrective measure to this problem. By using operational data to reconstruct real execution paths it gives leaders visibility into how work truly flows. Within the workflows, it exposes bottlenecks, hidden dependencies, and compliance gaps that traditional process mapping misses.
This article explains how AI process mapping works in practice, where it delivers value, where it fails, and how organizations can apply it strategically to unlock measurable outcomes.
What Is AI Process Mapping?
AI process mapping is a data-driven approach to discovering, visualizing, and analyzing how business processes actually operate across enterprise systems, based on real execution data rather than interviews or static documentation.
Instead of relying on manual workshops or flowcharts, AI process mapping ingests event data from systems such as ERPs, CRMs, finance platforms, supply chain tools, and workflow applications. Machine learning techniques reconstruct end-to-end process paths, revealing the true sequence of activities, decision points, delays, rework loops, and exceptions that occur during daily operations.
This is fundamentally different from traditional process mapping. Manual maps tend to describe intended workflows. AI process mapping exposes execution reality, including informal workarounds, regional differences, compliance deviations, and process drift that accumulate over time.
In practice, AI process mapping empowers enterprises to:
- See how work flows across systems, teams, and geographies
- Identify where time, cost, and risk are introduced
- Understand which process variants are stable versus volatile
- Create a reliable foundation for automation, AI deployment, and process redesign
When done correctly, AI process mapping becomes the bridge between strategy and execution for AI and automation initiatives to be grounded in how the organization actually works.
What Business Problems AI Process Mapping Solves
AI process mapping isn’t a documentation exercise. It is a diagnostic capability designed to surface the root causes behind stalled transformation, failed automation, and underperforming AI initiatives. In practice, it addresses a set of recurring enterprise problems that traditional reporting and BPM tools struggle to expose.
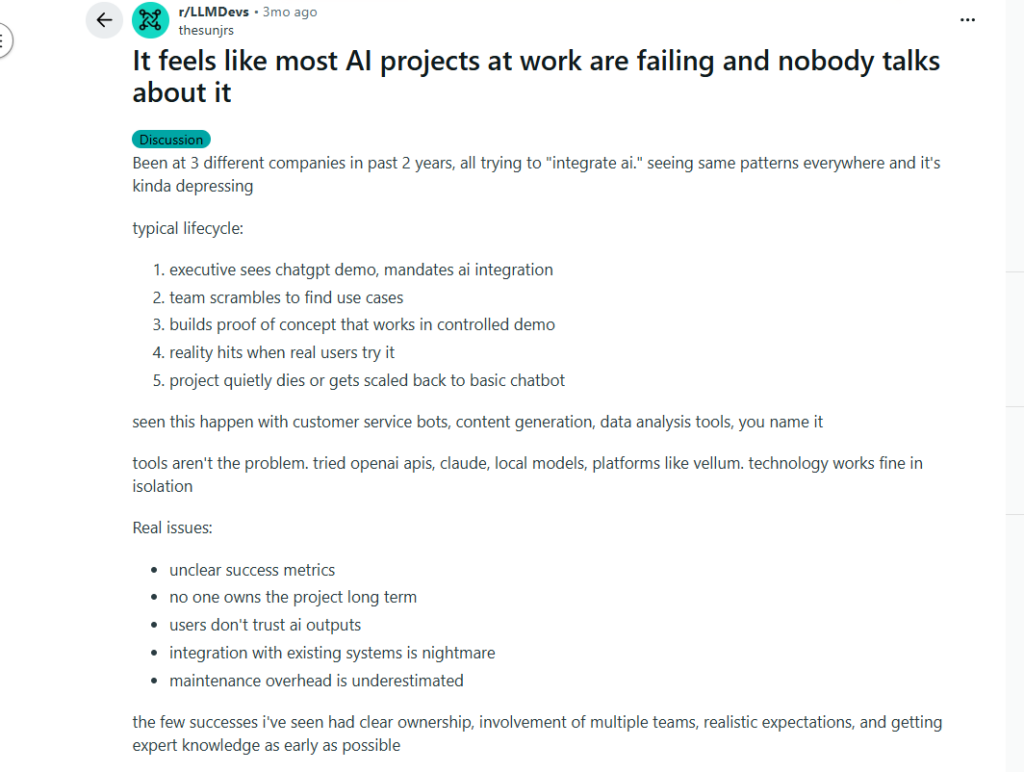
A Reddit thread talks about some real issues organizations face in AI implementation:
Hidden Bottlenecks and Cycle-Time Erosion
While dashboards may show aggregate performance, they rarely explain why work slows down. AI process mapping reconstructs real execution paths and reveals where approvals queue up, where rework loops occur, and where manual handoffs silently extend cycle times. This level of visibility allows leaders to target improvements with precision rather than guesswork.
Process Drift Across Teams and Regions
As organizations scale, the same standard process often evolves differently across geographies or business units. Process mapping makes these variants visible, highlights where deviations are harmless adaptations, and where they introduce cost, risk, or compliance exposure.
Compliance and Control Gaps
Organizations can see where required steps are skipped, controls are inconsistently applied, or exceptions bypass governance by looking into how processes are executed. This is especially critical in regulated environments where process adherence matters as much as speed.
Failed Automation and AI Initiatives
Failed attempts are often symptoms of poor process understanding. Many automation efforts collapse because they attempt to automate workflows that are unstable, overly complex, or poorly defined. AI process mapping exposes these weaknesses early, to make sure automation and AI are applied only where processes are ready to support them.
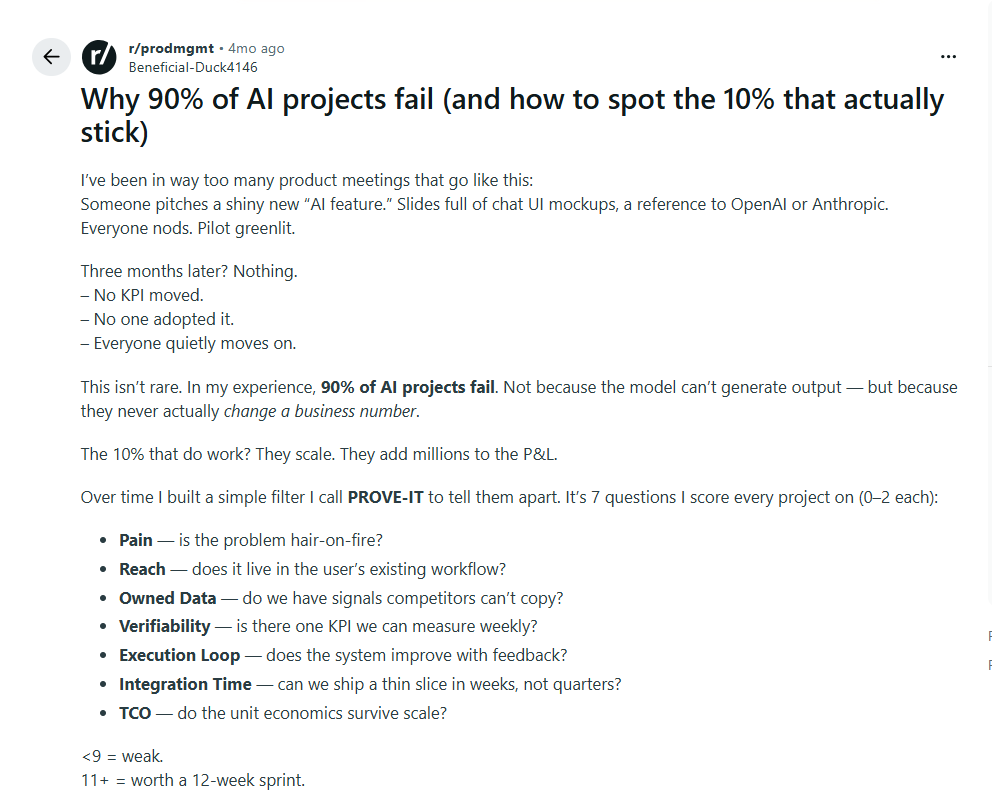
A Reddit chat discusses a simple filter PROVE IT to check if an AI project would be worth taking forward or scaling in the future:
Real-World Use Cases of AI Process Mapping
AI process mapping delivers value when it is applied to complex, cross-system workflows where traditional visibility breaks down. Across industries, enterprises use it to replace assumptions about ‘how work should happen’ with evidence of how work actually happens for targeted improvements and measurable impact.
Here are a few industries where AI process mapping sees real-world utility:
Finance and Operations
In finance and shared services environments, processes such as invoice-to-pay and order-to-cash often span multiple systems, including ERPs, approval tools, email, and manual interventions.
AI process mapping reconstructs these workflows end-to-end, exposing where invoices stall for review, where exceptions loop back repeatedly, and where compliance checks are inconsistently applied. Organizations use these insights to reduce cycle times, eliminate rework, and redesign approval logic before introducing automation or AI-driven decision-making.
Supply Chain and Logistics
Supply chains rely on tightly coordinated processes across planning, warehousing, fulfillment, and transportation systems. AI process mapping reveals how inventory actually moves across systems, where overrides occur, and how exceptions propagate during disruptions.
This helps leaders identify root causes of stockouts, late shipments, and manual firefighting to create a clear baseline before deploying optimization models or AI-driven planning tools.
Customer Operations
Customer support and service operations are rich with hidden complexity. AI-led process mapping analyzes ticket flows from creation to resolution, showing how issues escalate, where SLAs are breached, and how handoffs vary by team or region.
These insights allow organizations to standardize high-performing paths, reduce resolution time, and ensure AI copilots or automation are introduced into workflows that are stable and repeatable.
Real Estate
Real estate workflows are long-running and highly interconnected, spanning CRM, finance, legal, and property management systems.
AI process mapping helps organizations visualize leasing, underwriting, and closing processes as they actually unfold. It helps highlight approval delays, documentation bottlenecks, and compliance risks. At scale, it also reveals how processes vary across properties or regions, enabling consistent execution without sacrificing local flexibility.
Construction
In construction and field-heavy industries, processes are dynamic and rarely linear. Process mapping reconstructs project lifecycles from planning and permitting through execution and close-out, showing where change orders, inspections, or safety reviews disrupt schedules.
It compares planned workflows with actual execution for organizations to gain clarity on why timelines slip and where AI-enabled forecasting or automation can deliver real impact.
Across these use cases, AI process mapping is most valuable when it precedes automation and AI deployment. Teams that use it to stabilize and redesign processes first are far more likely to see sustained ROI from downstream AI initiatives. Implementation partners like RTS Labs play a critical role at this stage by helping enterprises translate process insights into redesigned workflows, automation strategies, and production-ready AI systems.
How to Implement AI Process Mapping in Your Organization
Successful AI process mapping isn’t a one-off analysis exercise but a structured initiative that turns operational data into decisions leaders can act on. Enterprises that see real value follow a disciplined rollout that prioritizes impact, data integrity, and ownership from day one.
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Processes First
Start where friction is most visible and costly. Look into finance close cycles, fulfillment delays, compliance-heavy approvals, or customer support escalations. Focusing on a small number of critical processes prevents analysis paralysis and ensures early wins that build executive confidence.
Step 2: Connect Data Across Core Systems
AI process mapping relies on event data from ERPs, CRMs, ticketing tools, workflow engines, and operational platforms. The goal is not perfect data, but connected data. Enterprises that invest early in integration and data alignment avoid misleading process reconstructions later.
Step 3: Discover and Visualize the Real Process
Using AI-driven discovery, organizations reconstruct how work actually flows through every variant, detour, and exception. This step replaces static assumptions with evidence, often revealing that the ‘happy path’ represents only a small fraction of real execution.
Step 4: Analyze Bottlenecks, Variants, and Risks
Once the real process is visible, AI highlights how time, cost, and risk concentrate in repeated rework loops, approval delays, non-compliant paths, or region-specific deviations. This analysis shifts discussions from opinions to facts.
Step 5: Prioritize Improvements Based on Business Impact
Not every inefficiency is worth fixing. High-performing teams rank opportunities by measurable outcomes, like cycle time reduction, cost savings, and compliance risk reduction, so effort is directed where ROI is clearest.
Step 6: Redesign Processes Before Automating
This is a critical and often skipped step. Stabilize and simplify workflows before layering automation or AI on top. Automating broken processes only scales inefficiency. Process redesign ensures downstream AI delivers compounding value.
Step 7: Operationalize Insights for Continuous Improvement
AI process mapping should feed ongoing optimization. Leading organizations embed insights into governance reviews, automation roadmaps, and performance management, creating a feedback loop where processes continuously adapt as conditions change.
Where AI Process Mapping Fails And Why
AI process mapping has enormous potential, but many organizations fail to realize it because of how it’s applied. These failures tend to follow predictable patterns that turn a powerful capability into an expensive reporting exercise.
Poor Data Quality and Incomplete Event Logs
When systems don’t consistently capture timestamps, handoffs, or decision points, AI reconstructs an incomplete or misleading version of reality. This leads teams to optimize symptoms instead of root causes.
Fragmented Systems and Partial Visibility
Mapping a process using only one or two systems, for example, ERP without CRM or workflow tools, creates blind spots where delays, rework, and compliance gaps actually originate.
Treating AI Process Mapping as a Tool
One of the reasons AI process mapping fails is when enterprises treat it as a tool rather than a transformation input. When insights live in dashboards but aren’t tied to decision ownership, governance forums, or improvement roadmaps, nothing changes operationally.
Lack of Process Ownership
Without clearly accountable owners, findings stall in analysis cycles, and recommended changes never move into execution.
No Concern for Workflow Redesign
Many organizations rush into automation without redesigning workflows first. Automating a broken or inconsistent process simply scales inefficiency, increasing cost and complexity instead of reducing it.
Top AI Business Process Mapping Tools in 2026
As interest in AI process mapping grows, enterprises typically encounter two very different approaches: tool-led platforms and expert-led services. To check which is the right choice for your organisation, figure out how deeply process insights must translate into execution and ROI.
Here are a few AI business process mapping tools you can use:
RTS Labs

RTS Labs offers AI process mapping as an enterprise service, building custom tool-led platforms suited to your needs accompanied with expert-led services.
RTS Labs approaches AI process mapping as a foundational capability for enterprise transformation. Instead of limiting discovery to event logs or screen recordings, RTS Labs combines AI-driven process discovery with deep data engineering, system integration, and domain expertise.
The approach is best suited for organizations that need process insights to directly inform automation, AI deployment, compliance improvement, and operational redesign across complex, multi-system environments.
RTS Labs partnered with a legal services organization to modernize how work gets done by embedding AI into key legal workflows. It mapped the organization’s AI processes to reengineer document processing, contract analysis, and knowledge retrieval. The client saw faster turnaround times, reduced manual effort, and improved consistency in high-value legal tasks.
The organization was able to reduce letter drafting time by 91%, from 120 minutes per letter to 10 minutes, once processes were in place.
RTS Labs is Best for
Enterprises seeking actionable process intelligence tied to execution, automation, and measurable outcomes.
Celonis
Celonis is widely known for process mining based on system event logs, particularly in ERP-centric environments. It provides strong visualization and benchmarking capabilities but typically requires significant internal effort to contextualize insights and drive change.
Celonis is Best for
Organizations with mature ERP data looking for self-service process analytics.
Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere integrates process discovery with RPA initiatives, helping teams identify automation opportunities. Its strength lies in automation enablement rather than holistic process intelligence across business units.
Automaton Anywhere is Best for
Teams focused primarily on identifying tasks for RPA automation.
Mimica.ai
Mimica.ai uses task mining and screen-level data capture to understand how work is performed at the user level. While useful for micro-task analysis, it often lacks enterprise-wide system context.
Mimica.ai is Best for
Analyzing individual or team-level task execution before automation.
KYP.ai
KYP.ai emphasizes operational efficiency and productivity analysis by combining process intelligence with workforce data. Its insights are strongest in identifying inefficiencies but require complementary expertise to drive redesign and scale.
KYP.ai is Best for
Organizations focused on productivity benchmarking and operational diagnostics.
AI Process Mapping: Off-the-Shelf Tools vs. RTS Labs’ Expert Service
Most enterprises evaluating AI process mapping can either deploy a tool or engage an expert-led service. While both approaches use AI to surface process insights, they differ significantly in how those insights translate into real operational change.
Off-the-shelf tools are designed for speed and accessibility. They help teams visualize processes quickly, flag inefficiencies, and explore automation opportunities. However, they often assume clean data, standardized systems, and internal teams capable of interpreting insights, redesigning workflows, and driving execution across departments.
RTS Labs takes a fundamentally different approach. AI process mapping is treated as an enterprise capability, tightly integrated with data engineering, architecture, governance, and execution. The focus is on understanding how processes run, followed by fixing, scaling, and embedding intelligence into daily operations.
Here’s a head-on comparison between off-the-shelf and custom expert-led services:
| Aspect | Off-the-Shelf AI Process Mapping Tools |
RTS Labs (Expert-Led Service) |
|---|---|---|
| Customization | Predefined models and templates | Fully tailored to business, systems, and industry context |
| Implementation Effort | Fast setup, high internal effort afterward | Accelerated delivery with hands-on expert ownership |
| Data Integration | Standard connectors; gaps are common | Deep integration across ERP, CRM, finance, operations, and legacy systems |
| Process Discovery | AI-driven, surface-level insights | AI-driven discovery plus expert interpretation and validation |
| Actionability | Insights require manual translation | Insights converted into redesign, automation, and AI roadmaps |
| Ongoing Improvement | Periodic analysis | Continuous optimization embedded into operations |
| Domain Expertise | Tool-agnostic, generic | Industry-specific expertise applied to process decisions |
| ROI Focus | Identifies inefficiencies | Prioritizes highest-impact, execution-ready improvements |
From AI Process Mapping to Process Intelligence: How RTS Labs Delivers Enterprise Outcomes
AI process mapping creates value only when it evolves into process intelligence that continuously informs decisions, automation priorities, and AI deployment across the enterprise. Many organizations stop at visualization. They can see how work flows, but they lack the mechanisms to translate those insights into sustained operational change.
RTS Labs differentiates itself from the rest here. RTS Labs approaches process mapping as the starting point of transformation by linking discovery directly to redesign, automation, and continuous optimization so insights translate into measurable enterprise outcomes.
This means process signals are connected to the systems that actually run the business so bottlenecks, compliance risks, and inefficiencies can be acted on in real time. Organizations gain a feedback loop where processes are continuously measured, refined, and optimized as conditions change.
The result is measurable impact with faster cycle times, reduced rework, lower operational risk, and AI initiatives that are built on how work actually happens.
If your organization is investing in AI, automation, or operational transformation, RTS Labs helps ensure those initiatives are grounded in real process intelligence. A focused AI process mapping engagement can be the difference between stalled pilots and scalable, ROI-driven execution — talk to our AI expert to explore what that looks like for your business.
FAQs
1. How is AI process mapping different from traditional process mapping?
Traditional process mapping documents how teams think work happens. AI process mapping uses system data to show how work actually happens—capturing exceptions, rework loops, delays, and regional variations that manual methods miss.
2. Is AI process mapping only useful before automation?
While it is critical before automation, AI process mapping is equally valuable after deployment. It helps monitor process drift, identify new bottlenecks, and continuously optimize workflows as conditions change.
3. What data is required to implement AI process mapping?
AI process mapping relies on event data from enterprise systems such as ERPs, CRMs, finance platforms, ticketing systems, and operational tools. The quality and consistency of this data directly impact the accuracy of insights.
4. Can AI process mapping support compliance and risk management?
By revealing skipped steps, unauthorized deviations, and inconsistent execution, AI process mapping strengthens auditability, compliance monitoring, and governance, especially in regulated environments.
5. When should an organization partner with experts instead of using tools alone?
Enterprises benefit from expert support when processes span multiple systems, involve regulatory constraints, or require redesign before automation. Execution partners help translate process insights into scalable operational change.






